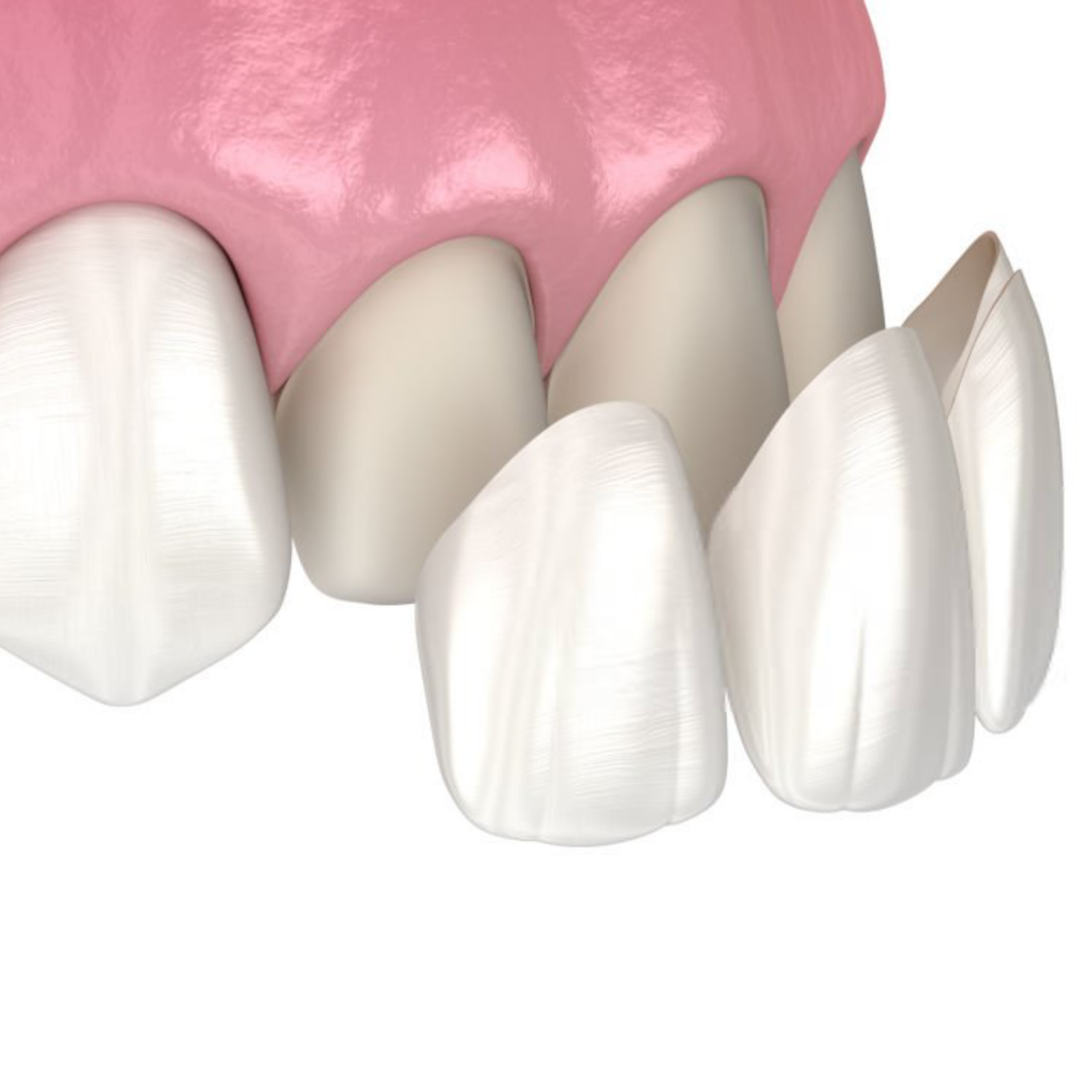
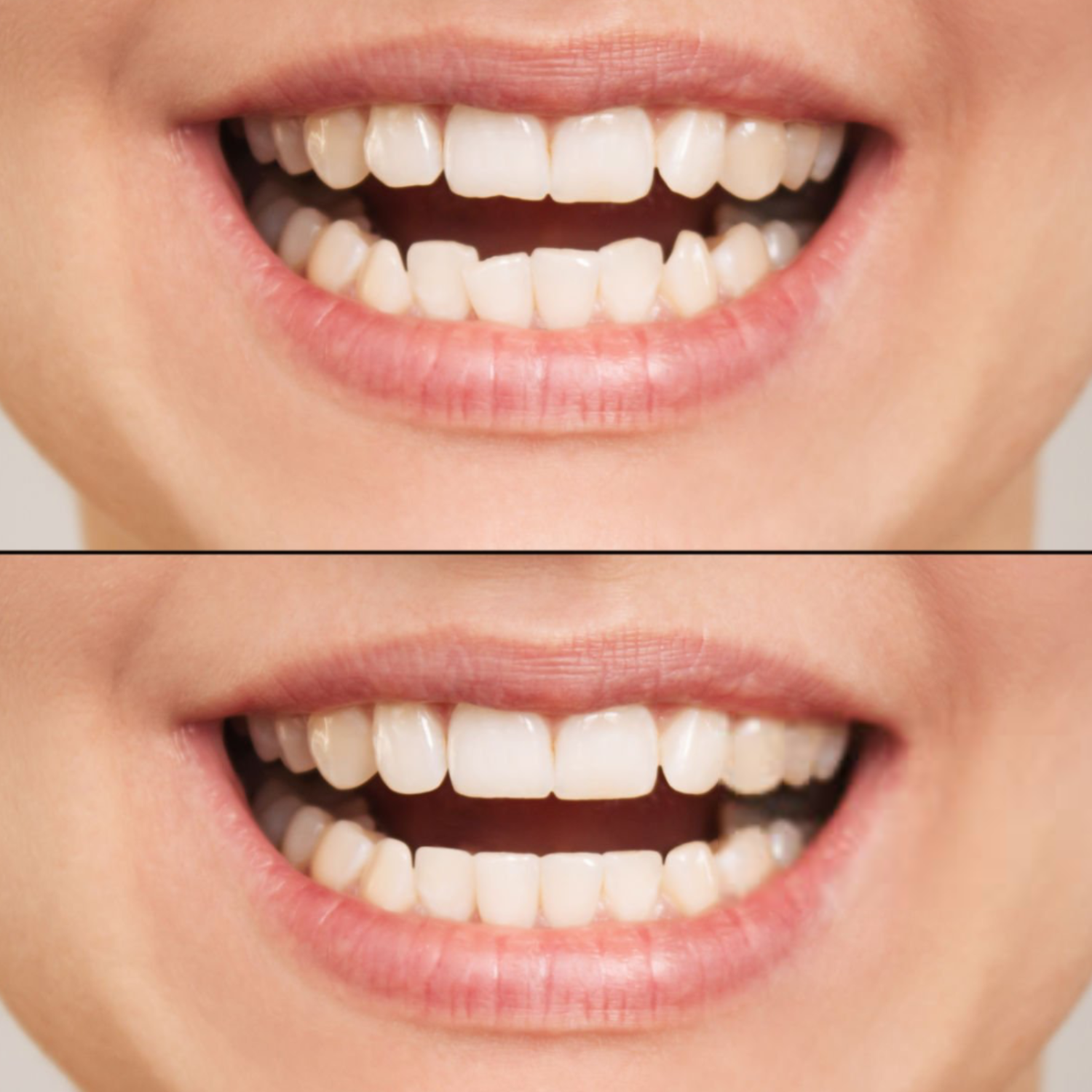
Cosmetic dentistry offers effective solutions for improving the appearance of teeth affected by discolouration, chips, gaps, or irregular shape. Two of the most commonly requested treatments are veneers and composite bonding. Although both aim to enhance the smile, they differ significantly in materials, clinical approach, longevity, maintenance requirements and suitability.
This article provides a comparison of veneers vs composite bonding, helping patients understand how each treatment works and which option may be more appropriate for their individual needs.
Veneers are widely used in cosmetic dentistry to address:
- Severe or intrinsic tooth discolouration
- Worn or uneven teeth
- Fractured teeth
- Gaps between teeth
- Minor alignment irregularities
- Where orthodontics is not desired or suitable
Types of intrinsic tooth discolouration may include fluorosis, trauma-related pulpal damage, age-related dentine darkening, developmental enamel defects (such as hypoplasia), medication exposure during tooth development (e.g. tetracycline or doxycycline), or teeth that have undergone root canal treatment.
Veneers are often considered a definitive cosmetic solution due to their durability and superior aesthetics.
CLINICAL PROCESS
- A small amount of enamel is typically removed to ensure a precise fit and long-term bonding
- Digital scans or impressions are taken
- Veneers are fabricated in a dental laboratory by skilled dental technicians
- Final placement occurs at a subsequent appointment following a try-in and shade assessment
EVIDENCE AND LONGEVITY
Clinical studies indicate that porcelain veneers can last 10–15 years or longer when placed correctly and maintained with good oral hygiene. Their ceramic composition makes them highly resistant to staining from tea, coffee, red wine and smoking.
Composite bonding is commonly used for:
- Small chips or fractures
- Closing minor gaps
- Improving tooth edges
- Subtle cosmetic enhancements
- Where conservative treatment is preferred
CLINICAL PROCESS
- Usually, no enamel removal is required
- The resin is applied, shaped and hardened using a curing light
- Treatment is often completed in a single visit
EVIDENCE AND LONGEVITY
Composite bonding typically lasts 3–7 years, depending on oral habits, bite forces and maintenance. Unlike veneers, composite resin is more susceptible to staining, chipping and surface wear over time, though repairs are straightforward.
One advantage of composite bonding is repairability, as small defects can often be corrected without replacing the entire restoration.
There is no universally “better” option — the choice depends on clinical, aesthetic, personal lifestyle factors and long-term goals.
Veneers may be more suitable if:
- You want a long-term cosmetic solution
- Teeth are heavily discoloured, worn or structurally compromised
- Maximum aesthetic refinement and colour stability is required
Composite bonding may be more suitable if:
- Changes are minor or conservative
- You prefer a reversible treatment or additive treatment
- Budget or time is a consideration or you are exploring cosmetic dentistry for the first time
A comprehensive dental examination is essential before deciding, as underlying tooth structure, bite alignment, gum health, parafunctional habits and oral health all influence suitability.